Light-emitting diode (LED) lamps are characterized by many parameters responsible for high-quality and safe lighting. The article will discuss the main characteristics of devices of this class, including comparing the latter with those of traditional incandescent lamps, and will also give recommendations on choosing LED lamps for the home.
- What is luminous flux?
- The strength of the luminous flux and how is it measured?
- The device and principle of operation of LED-lamps
- Main characteristics
- LED lamp power
- Scattering angle
- Created luminous flux
- Colorful temperature
- Ripple factor
- Equivalent power
- Working voltage
- Color rendering index
- Brightness control
- Heating and heat generation
- Comparative characteristics of LED devices and incandescent lamps
- Light output
- Heat dissipation
- Life time
- efficiency
- Price
- Environmental component
- Tips for Choosing an LED Bulb
What is luminous flux?
A luminous flux is a physical quantity that characterizes the number of “light” units of power of the corresponding radiation flux. Light power, in turn, is the energy passing through some space in a certain amount of time.
Simply put, a luminous flux is a concept that determines the amount of light emitted by a source (in the framework of the article, this is a light device), and how this radiation flux is emitted and distributed in space.
The strength of the luminous flux and how is it measured?
When evaluating and comparing lighting devices, such a unit of measurement of the luminous flux as lumen is used. This is the basic unit of measurement emitted by a source, the flux of light. Meanwhile, it is a mistake for lighting professionals and general users to evaluate lighting equipment using the concept of “brightness”. This term is not only erroneous, but can also be misleading, especially when it comes to LED lamps.
Traditional incandescent lamps emit in the widest possible spectrum of the light signal, while LED lamps “cover” only a narrow part of its “blue” area. But at the same time, emitting an approximately comparable amount of energy, the LED source shines brighter.
With regard to LED lamps, the concept of “illuminance” is sometimes used (characterizing the intensity with which light falls on the surface). The accepted unit of illumination is lux (lx).
The device and principle of operation of LED-lamps
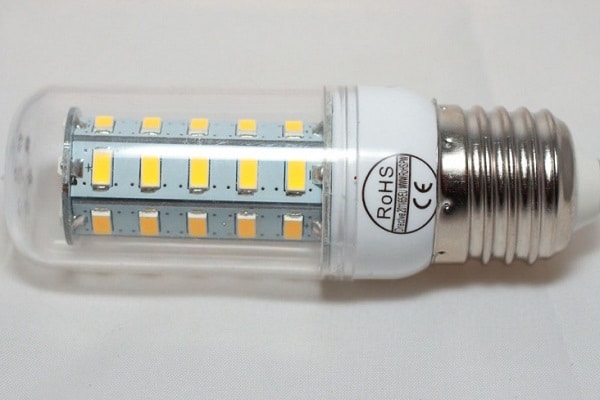
LED lamps for lighting differ only externally, the internal structure of different devices is approximately the same. The light is directly emitted by LEDs, the number, power and color spectrum of which varies depending on the model.
The principle of operation of the LED lighting lamp is based on the conversion of the mains alternating voltage, by means of an electrical circuit, into a constant one, which actually feeds the radiating crystals.
The household LED lighting device consists of the following components:
- The diffuser is a special hemisphere that increases dispersion and evenly scatters the light flux. Depending on the model, this component can be made of matte, transparent or translucent plastic (an exception is fluorescent devices, where a special reflective element is used).
- The LED crystal is the basis of the modern LED lamp. Their number can vary from one to several dozen – it depends on the design, dimensions, power, size of the heat sink of a particular model. It is the quality of LED crystals that determines the main parameters of the device and its durability, because if even one chip fails, the lamp can be thrown away.
- Printed circuit board – in its manufacture, a special anodized aluminum alloy is used, which allows it to effectively interact with the radiator, dissipating heat.
- The heatsink is a specially shaped aluminum product that allows more efficient removal of heat from the crystals. The heat-removing area of the radiator increases due to the presence of many plates on the body of this element.
- The driver is an important component of the circuit, without which the LED crystals would simply burn out. The unit rectifies, reduces and stabilizes the mains voltage. There are remote and built-in drivers – most of the household LED lighting devices are equipped with the latest type of devices mounted directly in the lamp housing.
- A capacitor is a radio-technical component that additionally smooths out voltage ripples supplied to the LED matrix.
- The polymer base of the base part is a structural element necessary to protect the body of the device from electrical breakdown and a person from electric shock when changing the lamp.
- Plinth – a switching part that provides connection to the mains. Most often, the base is made of nickel-plated brass, which provides reliable contact and anti-corrosion effect.
It is worth saying that in LED devices, unlike traditional incandescent lamps, the maximum heating zone is based on the inside. For this reason, the LED lamp requires effective internal cooling, which is implemented in the form of a cooling radiator.
Main characteristics
In many respects, LED devices are superior to incandescent lamps and other light sources. Among several dozens of technical parameters of LED lamps, several main ones can be distinguished.
LED lamp power
Under the power of the LED device, they mean the electrical power consumed by it from the network. To make it easier for the consumer to navigate, the equivalent indicator of an incandescent lamp is indicated on the packaging of the LED lamp.
Scattering angle
The luminous flux of household LED lamps is scattered at an angle of 60° – 340°. Devices with a less wide radiation pattern are used in the design of spot lighting, zoned lighting. Devices with a wide dispersion angle are used to organize general lighting. The largest angle of dispersion is available for lamps with LED filaments. The indicator for this type of device correlates with traditional incandescent lamps.
Created luminous flux
The brightness of the lighting device, or rather the amount of light emitted by it, is characterized by such a parameter as “luminous flux”, as already mentioned, measured in lumens. An LED lamp emitting a luminous flux of 400 lumens is approximately equivalent to a 40-watt incandescent lamp. In practice, there is a tendency for manufacturers of LED devices to deliberately overestimate this characteristic. Parameters that are close to real for specific devices can be found by examining the results of independent tests.
Colorful temperature
The more familiar incandescent lamp emits a pleasant soft yellow light, the color temperature of which approaches 2750 Kelvin (K). Accordingly, an LED lamp with the same color temperature will give the closest glow to a traditional lamp. For the most part, LED devices are characterized by a color temperature of 3000 K – with a fairly comfortable for the eyes, but slightly whiter light. Lamps with an indicator of 3000 – 4000 K are suitable for offices. Lighting devices with a color temperature of 5000 K or more are suitable only for utility rooms.
Ripple factor
This characteristic applies to all lighting devices. High-quality LED devices have a very low ripple factor, which is 3 to 5 times lower than incandescent lamps. According to this indicator, LED devices are allowed to be used in any premises. In inexpensive lamps, very often the ripple coefficient is not indicated, however, the flicker intensity is easily checked using the phone’s camera. In the presence of ripples, dark stripes are visible on the display.
Equivalent power
On the packaging of an LED lamp, there is also usually such a parameter as the equivalent power of an incandescent lamp. For example, it can be information that the LED device has a power of 5 W, equivalent to the power of an incandescent lamp of 40 W. Not too conscientious manufacturers can be tricky in the case of these parameters, so it is recommended that you first of all pay attention to the characteristic of the luminous flux of the LED lamp.
Working voltage
The standardized operating voltages of modern LED lamps are 220 V (for normal mains) and 12 V (for use with power supplies). The latter operate on both AC and DC voltages. However, some of these lamps, when powered by an alternating current source, may have too high a ripple factor that is harmful to the eyes.
Color rendering index
The spectral color rendering index of an LED device is different when compared with an incandescent lamp. It has more of a blue color component. The color rendering index (Ra), specified by the device manufacturer, characterizes the uniformity of the level of all color components. Luminous flux with a low index (less than 80 Ra) is unpleasant for the eyes. Incandescent lamps and sunlight have this indicator in the region of 97 – 98 Ra, high-quality LED lamps are more than 80, individual models – 90 units. In practice, the spectral color rendering index is deliberately overestimated by some manufacturers: when labeled on Ra – 80 packaging, it can be 75 or even less units.
Brightness control
Most LED lamps do not work with dimming devices designed to adjust the brightness of lighting fixtures. However, LED luminaires can be found on the market that already have a built-in dimmer unit, or they have the option of supporting external dimmers for incandescent lamps or specifically designed for diode devices.
Heating and heat generation
The luminous flux of the LED is directed in one direction, while heat is emitted in the other direction. For this reason, the interior of the LED lamp must be actively cooled. To do this, the lighting device is equipped with a radiator.
Comparative characteristics of LED devices and incandescent lamps
For a visual comparison of LED devices and incandescent lamps, you should refer to a special table. As you can see, the difference in power consumption between these classes of devices with the same luminous flux strength is significant.
| Incandescent lighting fixtures, W | LED lamps, W | Light flux strength, Lm |
| 25 | 3 | 250 |
| 40 | 5 | 400 |
| 60 | eight | 650 |
| 100 | fourteen | 1300 |
| 150 | 22 | 2100 |
But in fact, a 5W LED fixture is not equivalent to a 40W incandescent light bulb. The illuminance of an LED device can actually be far from 400 lumens depending on several factors. This, for example, is a matte case, “devouring” part of the power by the driver, other electrical components, etc.
Light output
One of the most important parameters in the calculation of the lighting scheme of the room is the light output of the mounted device. This characteristic is measured in Lumens / Watts. In incandescent lamps, the light output is from 8 to 10 lm/W. In LEDs, the parameter ranges from 90 to 110 Lm / W, and in high-quality models – from 120 to 140 Lm / W. In terms of light output, LED luminaires are 8-10 times better than alternative options.
Heat dissipation
When comparing LEDs and traditional incandescent lamps, their heat dissipation should be taken into account. Glass bulbs of incandescent lamps heat up to 230 – 240 degrees Celsius, while a powerful LED lamp can heat up to a maximum of 45 degrees. For this reason, the latter are not fire hazardous and can be mounted in any room, unlike incandescent lamps, which are not recommended for use, for example, inside wooden structures.
Life time
The main characteristic that speaks about the advantage of LEDs. An LED matrix can operate for 40,000 hours, while an incandescent lamp rarely lasts more than one thousand hours, which is almost 40 times less. For the sake of fairness, it should be noted that such high rates are inherent in high-quality LED products from well-known manufacturers. Cheap LED crystals have a much lower resource.
efficiency
Lamp efficiency is a concept that characterizes the amount of light produced relative to the thermal output of the device. This characteristic of LED devices approaches 90%, while, like incandescent lamps, the useful action is estimated at 7-9 percent. Needless to say, how much more economical LED lighting devices are in comparison with traditional counterparts.
Price
A much more controversial question is what is more profitable to use: diode lamps or incandescent lamps? Despite the fact that the former are an order of magnitude more expensive, their total operating time far exceeds the service life of the second option. And if we take into account such an indicator as energy savings, traditional lamps have no chance at all. In practice, however, things are not so clear cut. An LED device, like other types of lamps, can fail much earlier than its service life threshold (for example, during power surges or temperature changes). In addition, they shine weaker, so users often have to buy and install additional LED lighting.
Environmental component
Certified LED lamps contain a very small percentage of hazardous chemicals. They, like incandescent lamps, do not require specialized disposal. But this does not mean at all that expired appliances should be thrown away with other household waste. Lighting devices can be handed over, for example, to special collection points.
Tips for Choosing an LED Bulb
Choosing a good LED lamp is not an easy task. Sometimes world-famous manufacturers also have specimens with a high level of pulsations or with light output parameters that are overestimated relative to real values. The following recommendations are based on practical experience of users and the results of independent experts. A good LED lamp should meet the following criteria:
- ripple factor – no more than 30%;
- color rendering – index 80 and more;
- luminous flux level – corresponds to the value of the light flux of an incandescent lamp;
- acceptable lighting angle – no more than 50 degrees;
- if necessary, support for switches with an indicator;
- if necessary – support for dimming.
In addition, it will not be superfluous to focus on the following points:
- Put your hand under the light of the lamp. If the skin has a gray tint, the device uses LEDs with a low color rendering index.
- Even if you see the designation “no ripple” on the package, this does not mean that flicker is completely absent. Most likely its value lies within 5%.
- If it is possible to turn on the lamp, point the turned-on smartphone camera at it. If you don’t see any stripes, the LED fixture has a low pulsation level.
- Swipe a fountain pen in front of the turned on lamp. If the object doubles or triples, the source has a high level of pulsations.
- The brightness of the LED lamp can be checked using special light meter applications on your Android smartphone.
- Do not buy a product with a release date of 3 years or more. It is better to choose a more modern option.
- Choose an LED lamp with a long warranty period (3-5 years).
- Please keep your receipt so you can return or exchange the item if needed.
LED lamps differ from classic incandescent lamps in many characteristics. The most important of them are power, dispersion angle, luminous flux, color temperature and ripple factor. When choosing an LED lamp, you should also pay attention to the light and heat output of the device, its warranty period, efficiency, equivalent power, operating voltage and color rendering index.







Светодиодные лампы с холодным бело-синим свечением портят зрение. Покупать для дома нужно лампы с тёплым свечением или нейтральным белым светом. А вот для детей и тех, кто часто работает за столом, в настольную лампу офтальмологи рекомендуют ставить обычную лампу накаливания.
В доме стоят два вида ламп и дольше работают светодиодные, хотя перепады напряжения у нас постоянные. Для примера, на кухне стоит лампа накаливания, которую за полгода поменяли 4 раза, а в торшере, в гостинной – светодиодная, ею пользуемся больше года, при этом свет включаем в той и другой комнате одинаковое время. Так что всё-таки выгоднее светодиодные лампы, несмотря на более дорогую цену.
Хочу возразить комментарию Натальи.
Я, лично, ни разу не слышала от своего офтальмолога (а его я посещаю раз в пол года), информации о том, что светодиодные лампы с холодным свечением портят зрение.
У нас во всех комнатах стоят светодиодные лампы.
При выборе света такие лампы очень экономичны в использовании.
Мы переехали в свою новую квартиру еще в 2015 году и еще, пока что, ни разу не поменяли ни одной лампочки.
Всем конечно по разному, но нам нравится холодный свет. А желтый или белый – какой-то тусклый и не яркий.
А я только недавно в целях экономии электричества поменяла почти все лампы накаливания в частном доме на светодиодные лампы как раз с нейтральным белым светом. Только при этом пришлось заменить еще и те выключатели, в которых есть подсветка, так как они были причиной неполного выключения света в таких лампах.
В данной статье содержится много интересных практических советов по поводу того, как правильно выбрать светодиодные лампы. Я обязательно им последую и проверю качество своих ламп. Если что, придется купить более качественные.
Я очень довольна, что теперь есть такие лампы, реально экономят электроэнергию и платить за пользование ею становится дешевле. Но это не главный их плюс, реально нравится, что в квартире от них света становится больше и намного. А на счет того, что дампы портят зрение, так его все портит, будем откровенны. Я вот, например, совершенно не люблю лампы с теплым светом, мне они не дают нормальной яркости, мне так кажется. Всегда покупаю холодный свет, такие мне по душе больше пришлись. И всегда стараюсь купить мощные экземпляры. 💡
Технологии не стоят на месте. У них, большое преимущество. Во-первых потребление энергии немаловажно, освещение отличное. А то что, имеется и срок годности, считаю знаком качества. У меня например световой поток не оказывает отрицательного воздействия на зрение. Глаза меньше болят. Их еще и можно сдать в пункты приёма, что является экологичный. Полагаю важно, что лампы могут работать как от переменного, так и от постоянного напряжения. Думаю такие лампы должны быть у каждого человека. Выбирайте экологичные лампы.