Prices for energy resources, including electricity, are quite high, so consumers are interested in LED lamps. And lower prices for these economical lamps only contribute to increased demand. The main thing is to choose the right light bulb from the range presented – the products differ in price, parameters, reliability.
- Features of LED light bulbs
- Pros and cons of LED lamps
- What are the types?
- Criterias of choice
- Light flow
- Power
- Supply voltage and frequency
- Plinth type
- Colorful temperature
- Scattering angle
- Dimmable
- Ripple factor
- Operating temperature range
- Color rendering index
- Moisture and dust protection
- Product life
- Flask type
- Weight and dimensions
- How do LED lights shine?
- Rating of the best LED bulbs
- Philips
- Osram
- Gauss
- Feron
- camelion
- How to switch to LED lamps?
Features of LED light bulbs
A light-emitting diode lamp (LED), unlike a conventional incandescent bulb, is a complex electronic device consisting of several dozen parts. The operation of the lamp depends on the quality and parameters of the latter – how good and safe it will give light, and how long it will work.
As part of any LED lamp, there is a semiconductor crystal that generates light, and a driver is an electronic circuit that converts 220 V AC to 12 V DC.
The main elements of the LED lamp and their features:
- Plinth. With it, the lamp is screwed into the lamp socket. Plinths are usually made of brass coated with an anti-corrosion nickel compound. There are also lamps with pin bases – for certain types of lamps and needs.
- Radiator. With its help, heat is removed from the LEDs. Also, the task of radiators is to ensure the optimal temperature regime of operation. The material of manufacture is varied – from cheap plastic to expensive ceramics. The best option is composite materials and aluminum.
- Driver. Its task is to stabilize the voltage by converting AC to DC, as well as powering the LEDs. As part of the driver – a lot of microcircuits , capacitors, a pulse transformer. In budget lamps, there may not be a driver.
- Diffuser. This is a transparent flask that helps the light to scatter in space. Usually has the form of a hemisphere. Materials – plastic or polycarbonate. The flask also prevents moisture and dust from entering the housing.
- LEDs. They are the main working elements in the LED lamp. The glow appears during the operation of the diodes.
Pros and cons of LED lamps
LED lamps have long proven their superiority over the once traditional incandescent lamps. However, not all consumers have switched to economical lamps. A detailed analysis of the advantages and disadvantages of LED light bulbs will help you make a decision.
Advantages over incandescent lamps:
- low heating – you can touch the lamp without risking getting burned, which is especially important for families with children (when it comes to table lamps);
- savings – giving an equal amount of light with incandescent lamps, LED lamps consume electricity by an order of magnitude less;
- durability – LED lamps last 20-50 times longer than conventional ones;
- stability – the same brightness is maintained, despite power surges in the network;
- brightness – in a luminaire with a power limit, you can install an LED lamp that gives a brighter light than incandescent sweets.
Advantages over luminescent counterparts:
- environmental friendliness – no mercury;
- efficiency – less energy consumption with equal luminous flux;
- fast response – LED lamps ignite with lightning speed at full strength, and fluorescent lamps gain brightness from 20% to 100% in one minute at room temperature, even longer – at low temperatures;
- good spectrum – much closer to natural light than fluorescent counterparts.
Minuses:
- high price;
- a large number of low-quality products – with poor light quality;
- poor performance of some lamps equipped with switches and indicators;
- brightness adjustment is provided only in the most expensive models.
What are the types?
Manufacturers offer a large selection of a wide variety of LED lamps that differ in purpose, types of LEDs, and other parameters. Further, the classification of LED-lamps according to various criteria.
According to the field of application, lamps are distinguished:
- For home. Represent a flask on a standard socle. Suitable for any lamps.
- For the street. Produced using anti-vandal technologies, have a high degree of protection.
- For plants. They are used in the cultivation of indoor flowers, seedlings. In the spectrum of radiation – ultraviolet, accelerating the growth of plants.
- For decoration. Their main purpose is to decorate and stylize the interior. They are distinguished by a small scattering angle and a wide range of colors, create comfort and zone the room.
- LED spotlights. Installed in gardens and parks. They have a certain direction of light and a scattering angle.
LED type:
- SMD – point LEDs mounted on a substrate, on top of which a lens is placed. The number of crystals – 1-3 pcs. The design has good heat dissipation.
- COB – crystals are placed directly on the board. The construction is durable.
According to the color temperature of light:
- with daylight;
- with cold light;
- with warm light.

Plinth type:
- E – universal base “Edison”;
- G – pin bases;
- R – with recessed contacts.
In the form of a flask (the most common):
- Candle. Such lamps have a very limited scattering angle and low power. If they are used in chandeliers, then in large quantities. Moreover, the horns of the chandelier should be directed downwards. The best uses for candle lamps are table lamps and night lights.
- Pear. In appearance, they are very similar to standard incandescent lamps. They are used mainly in chandeliers with downward-pointing horns. If the luminaire has sockets oriented to the ceiling, part of the room will be in shadow.
Models equipped with spot LEDs have a beam angle of up to 180°, since all diodes are on the same side of the plate. - Corn . The flask is similar in shape to a corncob – it is elongated, cylindrical, and not much larger than the base. Yellow diodes are located on polyhedral substrates, and resemble grains on the cob.
Corn lamps scatter light well. They are used in horizontal lamps and in spot lighting with shading shades.
Criterias of choice
When choosing incandescent lamps, consumers were guided, as a rule, by only one parameter – power, measured in watts. The more powerful the bulb, the brighter its light. In LED lamps, much more parameters and characteristics have to be taken into account. Having understood them, it will be possible to select the optimal lamps for each specific case.
To choose an LED lamp that is most suitable for your goals, the information written in large letters on the package is not enough. You will have to familiarize yourself with the technical specifications printed in small print.
Light flow
In the era of incandescent lamps, consumers were not interested in the concept of luminous flux. The brightness of the lamps was determined by the power – the number of watts. It was previously and now indicated directly on the glass flask and on the packaging, if any.
Thanks to LED lamps, it was possible, by significantly reducing power, to increase the efficiency of devices. This allowed to save electricity and consumer funds.
What is a luminous flux and its features:
- designation – Ф, lm/lm;
- determines the amount of light energy that the lamp gives off;
- knowing the luminous flux, you can easily find an LED analogue to replace an incandescent lamp – according to the correspondence table;
- the color temperature affects the luminous flux – the higher it is, the greater the f.
Power
Lamp power is measured in Watts (W), denoted by the symbol “P” and indicates the amount of energy consumed per unit of time (hour). The most popular LED lamps are products with a power of 5 to 13 W – they correspond to incandescent lamps with a power of 40-100 W.
The total power consumption is the sum of the powers – the LEDs and the driver. Moreover, the latter consume no more than 10% of the power – if they are of high quality.
Supply voltage and frequency
Russian stores offer lamps designed for 12 V or 220 V. In a number of countries, a mains voltage of 110 V is provided, and lamps designed for it are not suitable for our consumers.
How to deal with stress:
- if there is an E mark on the base, this is a 220 V lamp;
- if G is a universal lamp, it is designed for both 12 V and 220 V.
Voltage is measured in Volts (V) and is denoted by the letter U. The parameter is usually indicated on the packaging in the form of a range – it is in it that the manufacturer guarantees the correct and safe operation of the lamp.
If, for example, it is indicated that the operating voltage of the lamp is in the range of 176–264 V, it is clear that it will safely withstand the most serious drops and power surges in the network without losing brightness. The operating frequency for LED lamps is 50/60 Hz.
Plinth type
Manufacturers offer LED lamps with different types of base, trying to meet the needs of consumers as much as possible. The most popular type of base is E27. This is a classic version that matches the base of conventional incandescent lamps.
Plinth types:
- E14 – minion;
- E27 – standard;
- E40 – for powerful lamps indoors and outdoors;
- G4 – to replace halogen lamps with LED ones;
- GU5.3, GU10, GX53 – for recessed and overhead luminaires in the ceiling, furniture;
- G13 – swivel type tubular base for T8 lamps.
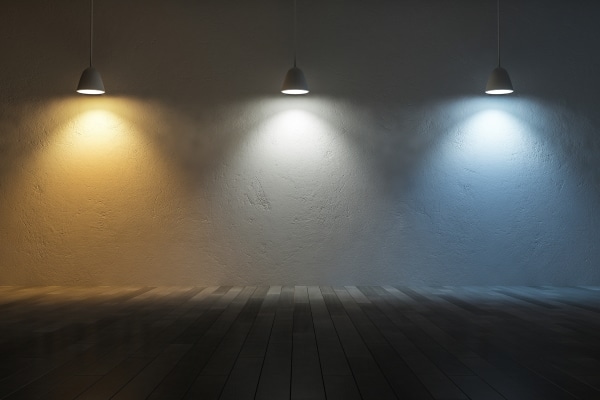
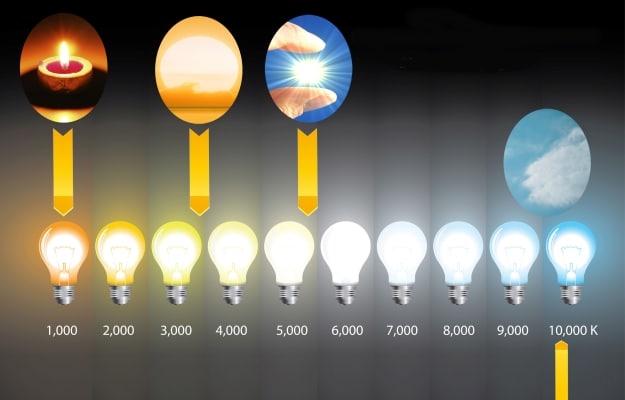
Colorful temperature
All incandescent lamps emit the same light, but LED lamps differ in the shade of radiation. The white glow scale is conditionally divided into neutral, warm and cold light.
Color temperature of LED lamps:
- 2700-3200K – warm light. Corresponds to the glow of incandescent lamps. Calms and creates a cozy atmosphere.
- 3 200-4 500K – neutral light. It is as close as possible to natural daylight. Ideal for illuminating work areas.
- From 4 500K – cold light. They give off a blue-white glow. Used in work areas. Where high concentration and focus on the work performed is required.

Scattering angle
This parameter affects the propagation of light in space. It is determined by the design of the diffuser and depends on how the LEDs are located. The norm is from 210 degrees.
If you need backlighting for work related to small elements, it is recommended to purchase a lamp with a scattering angle of 120 degrees.
In luminaires designed for general lighting, lamps with maximum beam angles are required. And for table lamps, on the contrary, choose products with the minimum values of this indicator.
Dimmable
Dimmers are modules designed to control the brightness of the light flux, and allow you to change the brightness of the glow. However, not all LED lamp drivers are capable of supporting this option.
The cost of dimmable LED lamps is higher than conventional ones, since their electronic components are more complex. An ordinary LED lamp connected to a dimmer will not shine. Or it will flash.
Ripple factor
Due to the pulsation of light, eyes get tired and general well-being worsens. Therefore, it is so important to purchase and use lamps that do not have visible ripples (according to SNiP, they are acceptable at the level of 5-20%).
You can check the lamp for pulsation using a smartphone – look at the light that it emits through the camera. If there is ripple, stripes will appear on the display.
Only some manufacturers indicate in the list of characteristics the parameter Kp – the ripple factor. In fact, this is an extremely important characteristic on which the health and well-being of a person depends.
Recommendations for the pulsation factor of LED lamps:
- Kp of lamps powered by a network with a stable direct current is 0.
- The highest quality LED lamps are considered, in which the Kp is less than 20%.
- Lamps in which current drivers are installed have a Kp of no more than 1%.
Kp can be determined using an oscilloscope. First, the amplitude of the variable part of the signal on the LEDs is measured, and then it is divided by the voltage from the output of the power supply.
Operating temperature range
This parameter is especially important when operating lamps outdoors or in unheated production halls. There are models of LED lamps that work correctly in a certain temperature range. The default rate is from -30°C to +60°C.
In many regions of Russia, the temperature in winter drops much below -30 ° C, which means that for the street and unheated premises it is necessary to choose LED lamps that are designed for lower temperatures.
LED lamps should be used with caution in rooms with high temperatures, as well as near heat sources – in steam rooms, saunas, etc.
Color rendering index
This parameter is designated CRI or Ra and allows you to evaluate the visibility of the natural color of objects in the light emitted by LED lamps. The recommended index is Ra≥70.
Moisture and dust protection
This characteristic is described by alphanumeric designations – IPXX. Where XX is a pair of numbers indicating the degree of protection of the lamp. This parameter is not always listed, especially if the lamp is intended for indoor use.
Product life
The working period is somewhat abstract, since it, specified by the manufacturer, concerns the LEDs, and not the entire lamp. The operating time of LED lamps depends on the quality of the soldering of the elements, on how well the case is assembled.
Manufacturers, due to the long life of LED lamps, do not conduct full-scale tests to investigate the degradation of LEDs. Claimed hours of operation are 30,000 or more, this is just a theory, not actual numbers.
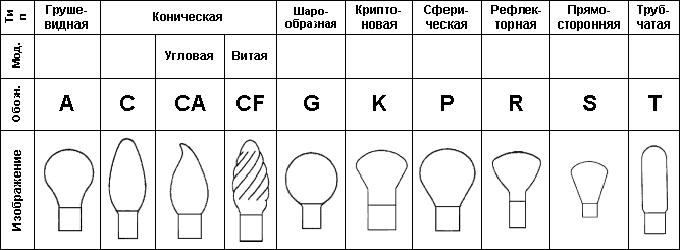
Flask type
The shape of the flask for most consumers is not a significant parameter, but in the characteristics it is often indicated in the first lines. As a rule, the bulb type is expressed in alphanumeric code.
The shapes of the bulbs of LED lamps and their designations are shown in the table below:
Weight and dimensions
The weight of an LED lamp is rarely of interest to buyers, but this parameter can be useful when it comes to a lightweight lamp.
Each manufacturer produces such LED lamps as it sees fit. Lamps produced by different brands can drastically differ in appearance, weight and size. For example, 10 W lamps from different manufacturers may have a difference in length and width of more than 1 cm.
How do LED lights shine?
The operation of an LED lamp is based on the physical processes that take place in semiconductors.
How LED lamp works:
- The glow occurs due to the passage of an electric current through the point of contact of semiconductors with different conductivity – n and p. One is dominated by electrons (n, with a negative charge), while the other is dominated by ions (p, with a positive charge).
- The semiconductor materials used allow electric current to flow in only one direction. When charged particles pass the boundary of semiconductors, recombination occurs – the transition of electrons to a different energy level. As a result, there is a glow visible to the eye.
- Simultaneously with the emission of light, heat is released, which is removed from the LEDs by means of a radiator.
Rating of the best LED bulbs
When choosing LED lamps, it makes sense to pay attention not only to their characteristics, but also to manufacturers. Among the many companies producing LED lamps, there are leaders whose products are in high demand, and their quality is not in doubt.
Philips
The company uses the latest technology, and its lamps are safe for the eyes – this is confirmed by laboratory tests. In the line – a model in which, by pressing a button, you can change the temperature of the glow. The company also produces super budget models – Essential.
The disadvantages of Philips products include the high cost of most models, as well as the narrow dispersion angle of cheap lamps.
Osram
This German company is one of the largest lighting manufacturers in the world. Represents a grandiose range of LED-lamps for a variety of fields and purposes. All lamps are characterized by excellent performance and economy.
The downside is the relatively high cost and the lack of a base for “intelligent” models (designed for direct connection). Whereas at Philips, for example, SmartSwitch models are equipped with the most ordinary plinth.
Gauss
Lamps of this manufacturer are distinguished by a long service life. He claims that his products last 50,000 hours – the lamps will be able to work for about 35 years. Warranty – 3-7 years. Basically, the company produces bright (from 900 lm) lamps with a neutral white color.
Feron
The manufacturer solved one of the most important problems of LED-elements – heating during operation, due to the special design of the radiator. Lamps from Feron almost do not heat up when glowing. The company offers a very wide range of products – it has lamps for any interior or engineering solutions.
Feron lamps feature good color rendering and low power consumption. But there are also disadvantages – imperfect reliability and the risk of buying a marriage.
camelion
Included in the TOP world manufacturers of lamps. Products are of the highest quality, wide range and a lot of unusual solutions. Camelion lamps last for a long time, give bright, flicker-free light and consume little energy.
How to switch to LED lamps?
The desire to save should not prevail over cold calculation. Do not rush to the store and buy LED lamps to replace all the incandescent bulbs in your home at once.
When switching to LED lighting, be guided by the following principles:
- Replace at first only the most powerful lamps – from 60 watts. Savings from replacing low-power lamps are small and the cost of LED-analogues may not pay off.
- Replace the lamps in those lamps that burn the most time during the day – in the hall, nursery, office. It makes no sense to change the lamps where they are rarely turned on – in change houses, utility rooms, etc.
- Do not buy many bulbs of the same company at once. Take 1-2 to try. Evaluate the spectrum and only then make a decision.
Manufacturers of LED lamps do not stand still – the market for their products is dynamically developing and improving. Being interested in the characteristics of LED lamps, their features and capabilities, you can not only save on electricity consumption, but also optimally solve the problem of lighting residential and non-residential premises, courtyards and gardens.